Get tips on how to meet your protein needs as a vegetarian
People often associate protein with animal meat and vegetarian with leafy greens and other plant foods. If you are about to start your healthy lifestyle journey, you may think that "high protein" and "vegetarian" don't go together. So, is it possible to have a high-protein vegetarian diet?
Going vegetarian does not necessarily mean that you'll miss out on your protein needs. With research and proper meal planning, it is possible to design a vegetarian diet that is not deficient in protein. Animal foods are not the only sources of protein, and many plant products are starting to serve as healthier alternatives.
This post will help you understand the following points concerning a high-protein vegetarian diet:
- Protein and amino acids
- Plant-based protein vs. animal protein
- How much protein should one eat per day?
- What is a high-protein vegetarian diet?
- What are the best sources of plant-based protein for vegetarians?
- Health benefits of high protein vegetarian/vegan diets.
- How to meet your protein needs as a vegetarian?
- Plant-based protein supplements for vegetarians/vegans?
- Who can take plant-based protein supplements?
- When can you take plant-based protein supplements?
Let's dig in!
About Protein
Protein is an organic substance made up of amino acids. It is deemed an essential macronutrient for its many roles in the body. Thus, this nutrient should not be missed out from the diet.
Aside from the muscles, protein is also found in the skin, bones, hair, gut, and antibodies.
The main functions of protein include building and repairing muscles and body tissues. It is for this reason that athletes and bodybuilders are focused on their protein intake.
The Amino Acids
Amino acids (the building blocks of proteins) are classified as either essential or non-essential. Of the 20 amino acids needed to form the proteins in the body, nine of these are essential.
When we say "essential," we refer to amino acids that cannot be produced by the body. Thus, we need to acquire them from food.
So, where can we get proteins? That would be from animals and plants.
Plant-based Protein vs. Animal Protein
Let's explore the difference between the two protein sources.
Animal-based proteins
For non-vegetarians, their primary source of protein is animal sources such as beef, pork, poultry, fish, and eggs. The protein found in animal sources is called "complete proteins." In this regard, plant sources often lack some essential amino acids, putting importance on proper plant food combinations.
Regarding nutrient content, animal-based sources (most especially meat) are rich in protein and fat, sodium, iron, and B-complex vitamins.
In fact, results from a 2021 meta-analysis show that animal-based proteins are better for supporting lean muscle mass and enhancing muscle strength.
However, moderate consumption of protein sources high in saturated fats and cholesterol is advised for individuals who are obese, hypertensive, and diabetic.
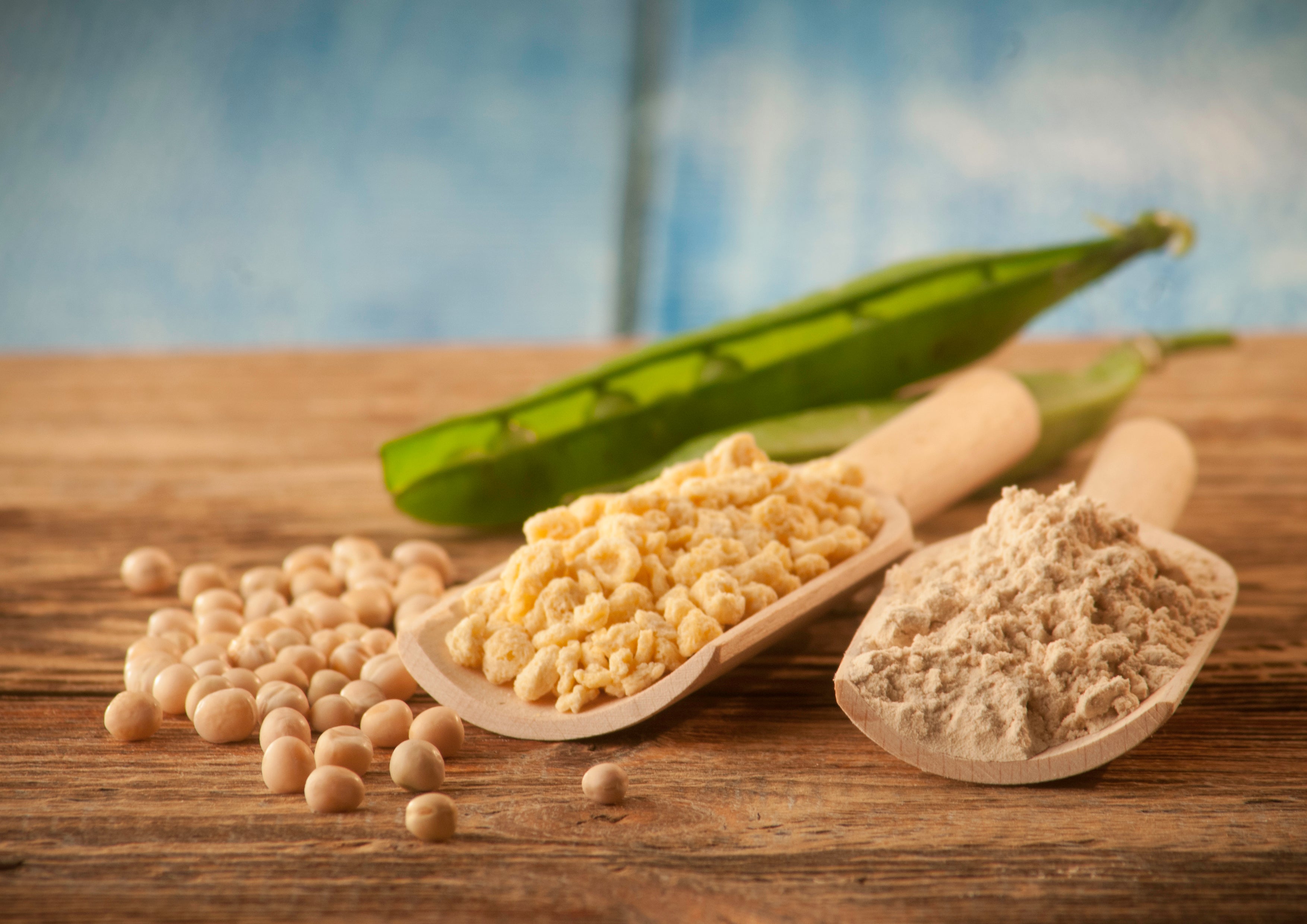
Plant-based proteins
The mixing and matching plant sources are advised to ensure no missing amino acids from the diet can be achieved through proper meal planning. Plant-based protein sources combined or eaten in a day to form complementary proteins are legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
Plant-based proteins have lower digestibility and a low amino acid profile. But according to a study, the protein quality of plant-based sources can be improved to increase its potential in helping build and maintain muscle.
On the one hand, plant-based sources of protein also happen to be excellent sources of fiber and a variety of vitamins and minerals. In addition, plant protein foods are packed with phytonutrients and antioxidants, which are known for many health benefits.
Strategies include adding the missing essential amino acids through fortification, plant breeding, combining different plant protein foods, and combining plant with animal-based sources.
In terms of sustainability, plant-based proteins are definitely more environment-friendly. Many people have since switched to a vegetarian diet which has a lower impact on the planet. A protein scorecard shows that beef, lamb, and goat have the highest greenhouse gas emission while wheat, beans, lentils, and nuts are among the lowest.
How Much Protein Should You Eat Per Day?
What Is A High Protein Vegetarian Diet?
A high-protein vegetarian diet will suit those looking for a sustainable and healthier alternative to their usual diet (which usually consists of high-fat meat).
It is common to think that a vegetarian diet's protein requirements are hard to meet. However, there is evidence that it can still supply adequate protein as long as a variety of protein-rich plant foods are eaten within a day.
High-quality proteins do not only come from animals. These can also be obtained from selected plant foods such as soy, quinoa, and chia seeds. These kinds of plant proteins are ideal for a high-protein vegetarian diet. However, indeed, most plant foods come short of one or two types of essential amino acids. Examples are wheat which lacks lysine, and legumes with low methionine content.
In order to maintain the nutritional adequacy of their diets, vegetarians are advised to eat various plant foods that complement each other. This way, the missing amino acids from one plant food can be obtained from another. Meal planning goes a long way in ensuring enough protein is supplied from a vegetarian diet.
What Are the Best Sources Of Protein For Vegetarians?
In adopting a high-protein vegetarian diet, you must ensure that you include plant foods containing high-quality protein to prevent protein deficiencies.
To determine the protein quality of foods, use the Protein Digestibility-Corrected Amino Acid Score (PDCAAS) tool. The food's protein quality is based on one's amino acid requirements and the ability to digest certain protein foods.
What are excellent sources of high-quality, high-protein foods that can be included in a vegetarian diet?
Legumes
First on our list of high-quality plant-based protein sources are legumes. These plant parts (leaves, stems, and pods) come from the Fabaceae family. Legumes have long been a part of classic vegetarian diets.
A study found that including legumes in the mix of a vegetarian diet removes the risk for protein deficiency.
What can you get from legumes aside from protein? Legumes are rich sources of folate, fiber, iron, phosphorus, and mono- and polyunsaturated fatty acids, which are all beneficial for health.
The table below shows the protein content of each type of legume per 100g.

Nuts
Nuts are defined as dry fruits containing a seed surrounded by a hardened ovary wall.
Aside from having high-quality protein, nuts are also rich in fiber, minerals, and unsaturated fatty acids. Along with legumes, including nuts in the vegetarian diet will ensure an adequate protein intake.
The table below shows the protein content of each type of nuts per 100g.


Whole Grains
The nutrient density of whole grains is attributed to its three layers: bran, endosperm, and germ. Each layer contains different vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals.
A study suggested the consumption of whole grains to help maintain protein balance in the body. Examples of whole grains included in the vegetarian diet are quinoa, brown rice, oats, wheat, buckwheat, and wild rice.

Some Vegetables
While most fruits and vegetables contain only a small amount of protein, some are actually good protein sources and can be included in a vegetarian diet. These are corn, broccoli, asparagus, brussels sprouts, and artichokes.

Other non-vegetarian foods
If you are a strict vegan dieter, you’ll surely only consume plant-based foods and avoid animal-based foods.
Note that being a vegetarian does not always mean that you can only consume foods coming from plants. In fact, following a strict vegan diet may be hard for many people.
If you’re someone who is open to welcoming a few dietary tweaks, you can include these foods:

Did you know? There are different types of vegetarian diets. These are vegetarian, fruitarian, flexitarian, pescatarian, lacto-ovo-vegetarians, Lacto-vegetarians, ovo-vegetarians, and strict vegans.
4 Health Benefits of High Protein Vegetarian Diet
#1 Decreases risk for heart disease
A meta-analysis revealed that replacing red meat with plant foods as a source of protein lowers the risk of developing heart disease. This healthy swap is explained further by a published study proving that nuts and seeds are better for heart health compared to animal protein.
#2 Reduces diabetes risk
The consumption of nuts and legumes is associated with a lower risk of diabetes. Furthermore, a study explored the potential of decreased diabetes risk from consuming vegetable sources for protein needs. Consequently, diets rich in red meat and processed meat are linked to developing type 2 diabetes.
#3 Aids in weight control
A study showed that consumption of chickpeas, beans, peas, and lentils promotes satiety or fullness, leading to good weight results. In another study, weight loss was evident among those who consumed peanut butter, walnut, and nuts compared with those who ate meat, chicken with skin, and cheese.
#4 Protects from some types of cancer
It has been reported by the World Health Organization that processed meats are carcinogenic. There is evidence that these foods can cause colorectal cancer if moderation in consumption is not followed.
Another study observed that the consumption of red meat is associated with breast cancer. While a diet consisting of other sources of proteins, including legumes and nuts, did not increase the risk for breast cancer development.
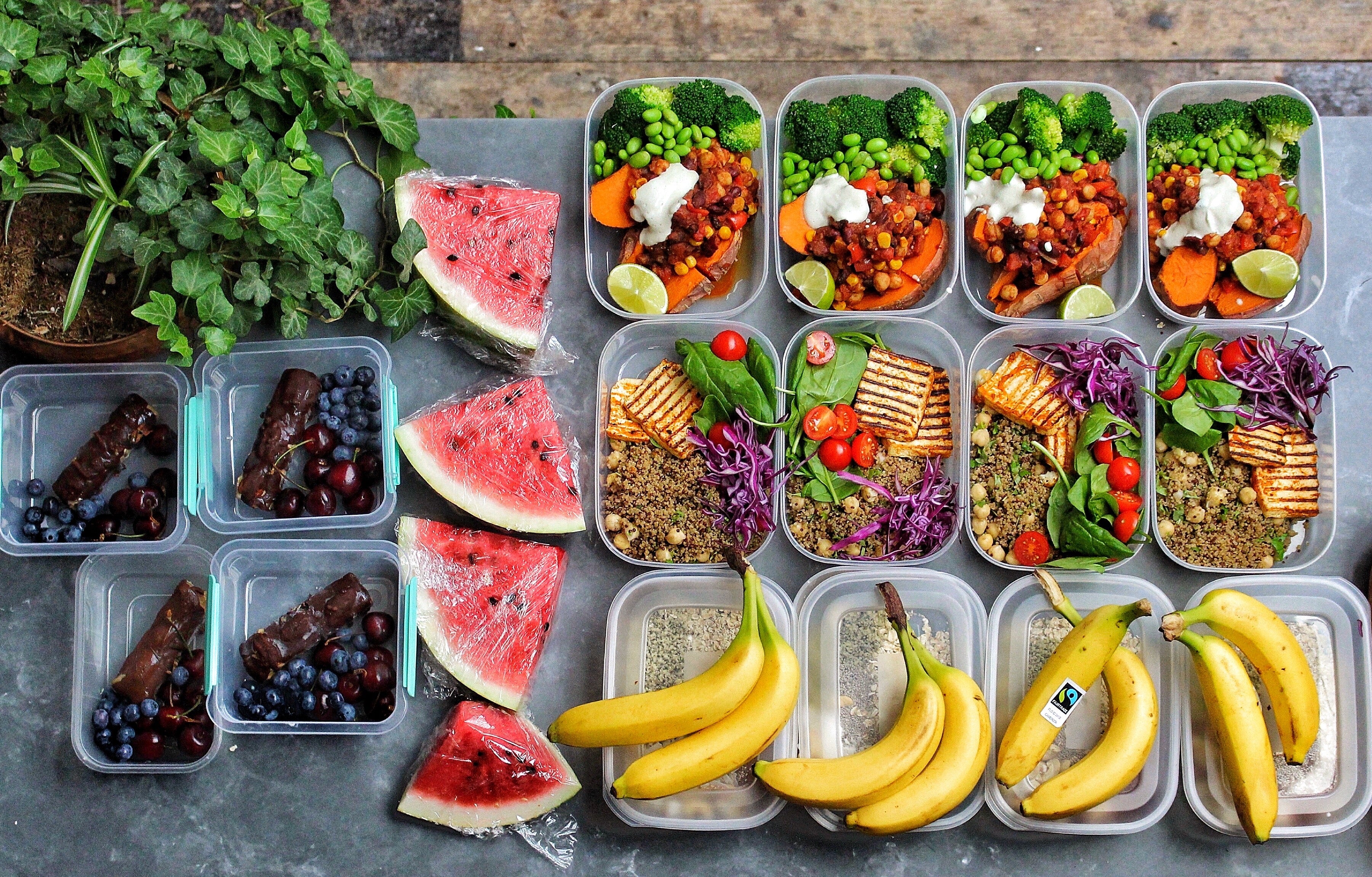
How To Meet Your Protein Needs As A Vegetarian?
Make sure each meal should contain protein.
Include a protein source at each meal, including snacks. Make sure that you balance your meals with good quality protein.
Breakfast
For breakfast, you need something that is filling and sustaining enough to kick-start your day.
Have a plate containing whole grains, nuts, seeds, tofu, sauteed bean, and vegetables. Try to be creative in matching which foods go well together.
For example, you can have a bowl of whole-grain cereal with berries (i.e., raspberries or blueberries) and oat milk.
Lunch
You might want to make a whole grain sandwich that has nut butter or tahini, baked tofu or tempeh, and some vegetables.
Include protein-rich soups, such as pea, bean, or lentil. If you want to have a protein-rich salad for lunch, you can add beans, tofu, nuts, and seeds to it.
Dinner
You can put an emphasis on having some protein-rich vegetables such as legumes and serve it whole grains or whole grain bread.
Alternatively, you can have some stir-fried tofu, seitan, or tempeh with veggies and grains.
Snacks
Nuts or seeds are great for snacks.
If you are having coffee, you may add your favorite plant-based milk to it. Or, make a smoothie containing soymilk, seeds, and your favorite fruit.
Read food labels
Food labels show you the essential nutrients that a product contains. In this case, check the product’s protein content. Food products that contain significant amounts of protein are found in plant-based milk, yogurts, cereals, bread, and other snack foods.
Are There Plant-based Protein Supplements For Vegetarians/Vegans?
Aside from the mentioned food sources, vegetarians and vegans can also get their supply of protein from supplements. The following are the different types of plant-based protein supplements that are commercially available:
- Pea protein
- Soy protein
- Hemp protein
- Pumpkin seed
- Sunflower seed
- Chia seed
Many of these are readily available in groceries and online. Thus, vegetarians and vegans will never run out of options regarding protein supplements suitable for their lifestyles.
Who Can Take Plant-based Protein Supplements?
Aside from the mentioned food sources, vegetarians and vegans can also get their supply of protein from supplements. Plant-based protein supplements are usually taken by
- Athletes
- Bodybuilders
- Vegans and vegetarians
- People who have limited access to whole protein foods
- People who need a convenient protein alternative
- People who are not getting adequate protein from diet alone
- Lactose-intolerant individuals
- Individuals who are allergic to animal protein sources
When Can You Take Plant-Based Protein Supplements?
The best time to take plant-based protein supplements depends on your health and fitness goals. If your goal is to lose weight, you may want to take your supplement between meals to promote satiety. This will lessen your caloric intake as you inch away from heavy meals.
On the other hand, if you aim to build muscle, protein supplements are recommended to take 15-60 minutes post-workout. Why? The post-workout phase is when the body utilizes protein at most, working harder to build and repair torn muscle tissues.
However, if you're simply targeting to maintain your muscle mass, it is best to spread your protein intake throughout the day. You can supplement your dietary protein with plant-based protein powder to ensure that you will not have any nutritional deficiency.
Our Take Away
Having sufficient protein intake is essential to maintaining bodily functions. Vegans and vegetarians can benefit from a high-protein vegetarian diet as more studies prove that this type of diet can supply adequate protein.
Various plant-based food sources offer high-quality protein, and a meal plan could help ensure that complementary proteins are consumed daily. Aside from proteins, one can reap many health benefits from this diet, such as a reduced risk for diseases and weight management.
If you're worried that you're not getting enough protein from food, many plant-based protein supplements are available on the market.
Thus, the best time to take these supplements varies depending on your health goals. You can consult a nutritionist-dietitian for a detailed meal plan that will suit your lifestyle.
Make Pea Protein As Part Of Your Healthy High Protein Vegetarian Diet!
Nuzest's Clean Lean Protein is a fantastic pea protein supplement that can go well with your high-protein vegetarian diet!
Our Clean Lean Protein is only made from premium quality European Golden Peas and provides the building blocks for vitality, repair, recovery, and muscle growth.
Clean Lean Protein is:
- 100% Vegan, gluten-free, lactose-free, GMO-free, and lectin-free
- Best for individuals with allergies or food sensitivities to animal-based and plant-based protein sources.
- Lectin-free to prevent leaky gut.
- Free from GMOs.
- Free from fillers, gums, and artificial preservatives.
How nutritious is pea protein? Find out here.
Why choose Nuzest's Clean Lean Protein from other pea protein powders? Discover the great news here.
Clean Lean Protein
Clean Lean Protein is powerfully plant-based and contains all nine essential amino acids.

Disclaimer:
The information provided on Nuzest is for educational and informational purposes only. The information provided on this site is not, nor is it intended to be, a substitute for professional advice or care. Please speak to your qualified healthcare professional in the event that something you have read here raises questions or concerns regarding your health.